Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) are two prominent cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant, each with unique properties and potential benefits. While both compounds have garnered significant attention in the health and wellness sectors, they differ in various aspects, including their chemical structure, psychoactive properties, health benefits, legal status, and methods of consumption. Let’s take a look at their different features and potential applications.
I. Chemical Structure and Origin
1.1 Chemical Structure
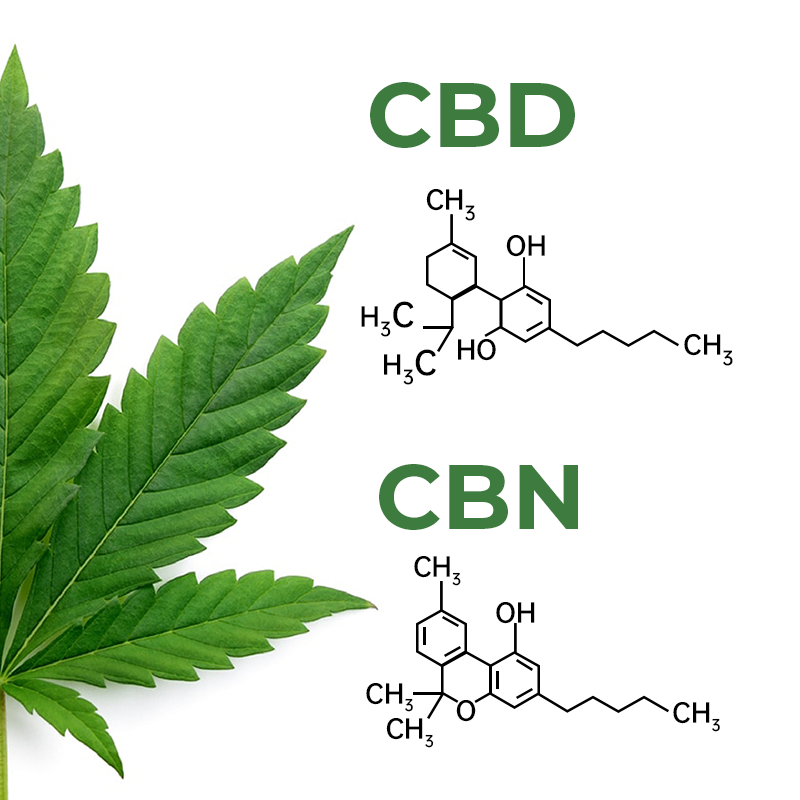
CBD and CBN share similar chemical structures, as both belong to the cannabinoid family. However, the way these compounds are formed within the cannabis plant differs significantly.
CBD: Cannabidiol is primarily found in hemp varieties of cannabis. It is a major cannabinoid, often comprising up to 40% of the plant's extract. CBD is synthesized from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) and remains stable when exposed to heat and light.
CBN: Cannabinol is typically produced from the degradation of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) when exposed to heat, light, or time. As a result, CBN is usually present in older or aged cannabis products. While CBN is often found in small quantities compared to CBD, it is still recognized for its unique properties.
1.2 Formation and Sources

The formation process of CBD and CBN plays a crucial role in their availability and effectiveness.
Sources of CBD: CBD is predominantly extracted from hemp plants, which are specifically bred to have high CBD content and low THC levels (usually below 0.3%). This makes hemp a popular source for CBD products, including oils, tinctures, and edibles.
Sources of CBN: CBN is generally derived from aged cannabis flowers that have undergone oxidation. This means that CBN is often found in older cannabis strains or in products that contain THC that has been stored for an extended period.
II. Psychoactive Properties
2.1 CBD's Non-Psychoactive Nature
One of the most significant distinctions between CBD and CBN is their psychoactive effects.
CBD: Cannabidiol is considered non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the "high" associated with THC. This property makes CBD a preferred option for those seeking therapeutic benefits without the mind-altering effects.
2.2 CBN's Mild Psychoactivity
While CBN is also classified as non-psychoactive, it does exhibit mild sedative effects, particularly when taken in higher doses.
CBN: Some users report experiencing a calming sensation when consuming CBN, which can aid in relaxation and sleep. However, this effect is much milder compared to THC and is often described as a gentle sedative rather than a high.
III. Health Benefits
3.1 Therapeutic Effects of CBD
CBD has been extensively researched for its various health benefits. Some of the most notable effects include:
Anti-inflammatory Properties: CBD is known for its potent anti-inflammatory effects, making it beneficial for conditions such as arthritis and chronic pain.
Anxiety and Stress Relief: Numerous studies have shown that CBD can reduce anxiety and stress levels, making it a potential treatment for anxiety disorders.
Epilepsy and Seizures: CBD has gained FDA approval in the form of Epidiolex, a medication used to treat certain types of epilepsy, demonstrating its effectiveness in seizure management.
Neuroprotective Effects: CBD has shown promise in protecting brain cells and may be beneficial in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.

3.2 Potential Benefits of CBN
While research on CBN is still emerging, preliminary studies and anecdotal evidence suggest several potential health benefits:
Sleep Aid: CBN is often praised for its sedative properties, making it a popular choice for individuals struggling with insomnia or sleep disturbances.
Pain Relief: Similar to CBD, CBN may also possess analgesic effects, although more research is needed to fully understand its efficacy.
Appetite Stimulation: CBN has been noted for its potential to stimulate appetite, which could be beneficial for individuals undergoing treatments that cause appetite loss, such as chemotherapy.
Antibacterial Properties: Some studies suggest that CBN may have antibacterial effects, potentially making it useful in combating certain bacterial infections.
IV. Legal Status
4.1 CBD Regulations
CBD's legal status varies by country and region, largely depending on its source.
Hemp-Derived CBD: In many places, CBD derived from hemp (containing less than 0.3% THC) is legal. This has facilitated the widespread availability of CBD products in health and wellness markets.
THC-Derived CBD: CBD extracted from marijuana plants, which contain higher levels of THC, may be subject to stricter regulations and is often only legal in jurisdictions where medical or recreational cannabis use is permitted.
4.2 CBN Regulations
CBN's legal status is less defined compared to CBD.
Lack of Clarity: Since CBN is a minor cannabinoid and less commonly discussed, its legal status often falls under the same regulations as THC. In some jurisdictions, CBN may be legal, while in others, it might be restricted due to its association with THC.
V. Methods of Consumption
5.1 CBD Consumption Methods
CBD is available in various forms, allowing users to choose the method that best suits their needs.
Oils and Tinctures: These are commonly used for their fast absorption and ease of dosing.
Edibles: CBD-infused gummies, chocolates, and other foods provide a tasty option for consumption.
Topicals: Creams and balms containing CBD can be applied directly to the skin for localized relief.
-Vapes: Vaporizing CBD oil offers quick onset effects, making it a popular choice among users.

5.2 CBN Consumption Methods
CBN is also available in various forms, though the market for CBN products is not as extensive as that for CBD.
Oils and Tinctures: Similar to CBD, CBN is often found in oil or tincture form for easy dosing.
Edibles: CBN-infused edibles are becoming more popular as a way to promote sleep and relaxation.
Vapes: Vaporizing CBN is another method of consumption, although less common than CBD vaping.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, CBD and CBN are two distinct cannabinoids with unique properties and potential benefits. While CBD has been extensively studied and recognized for its therapeutic effects, CBN is emerging as a promising compound, particularly for sleep and relaxation. Understanding the differences between these cannabinoids can help consumers make informed choices regarding their use. As research continues to evolve, both CBD and CBN may play significant roles in the future of health and wellness, offering a range of options for individuals seeking natural remedies for various ailments.