Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an acute respiratory infection caused by the influenza virus. It typically presents with symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, headaches, and fatigue. The flu virus is mainly transmitted through the air, primarily spread from person to person via coughing, sneezing, talking, or direct contact.
Key Characteristics of Influenza:
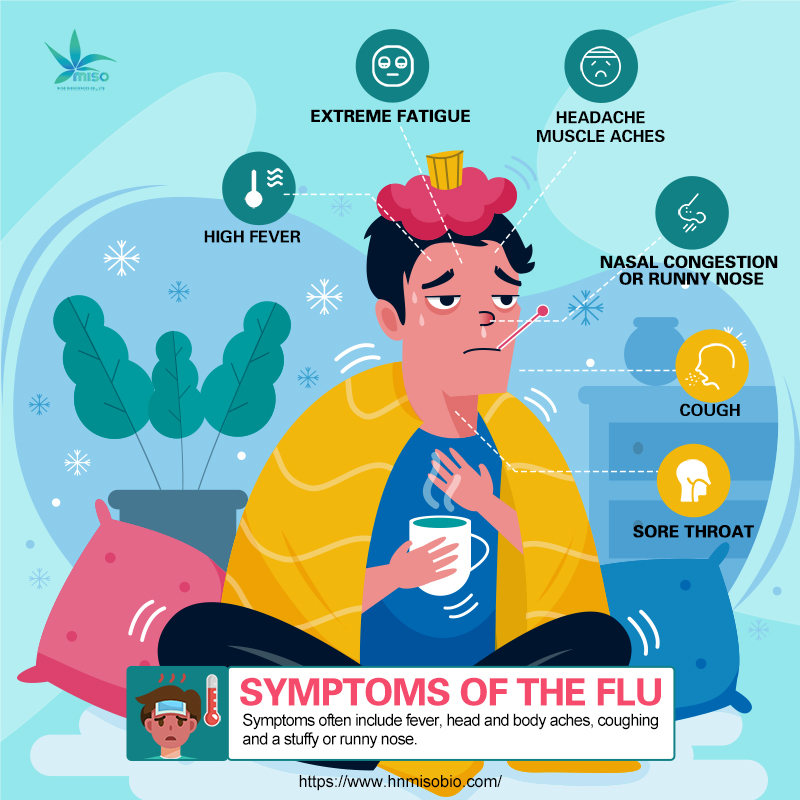
1. Symptoms:
- High fever: Often accompanied by chills.
- Cough: Dry or with phlegm.
- Sore throat.
- Headache, muscle aches: Feeling body pain.
- Extreme fatigue: May feel extremely weak and unable to get out of bed.
- Nasal congestion or runny nose.
2. Incubation period:
- The incubation period for the flu is usually 1 to 4 days, and infected individuals may spread the virus before showing symptoms.
3. Types of Influenza Virus:
- There are several different types of influenza viruses, with the most common being types A and B. Type A influenza viruses tend to cause wider outbreaks, while type B is more common during seasonal flu epidemics.
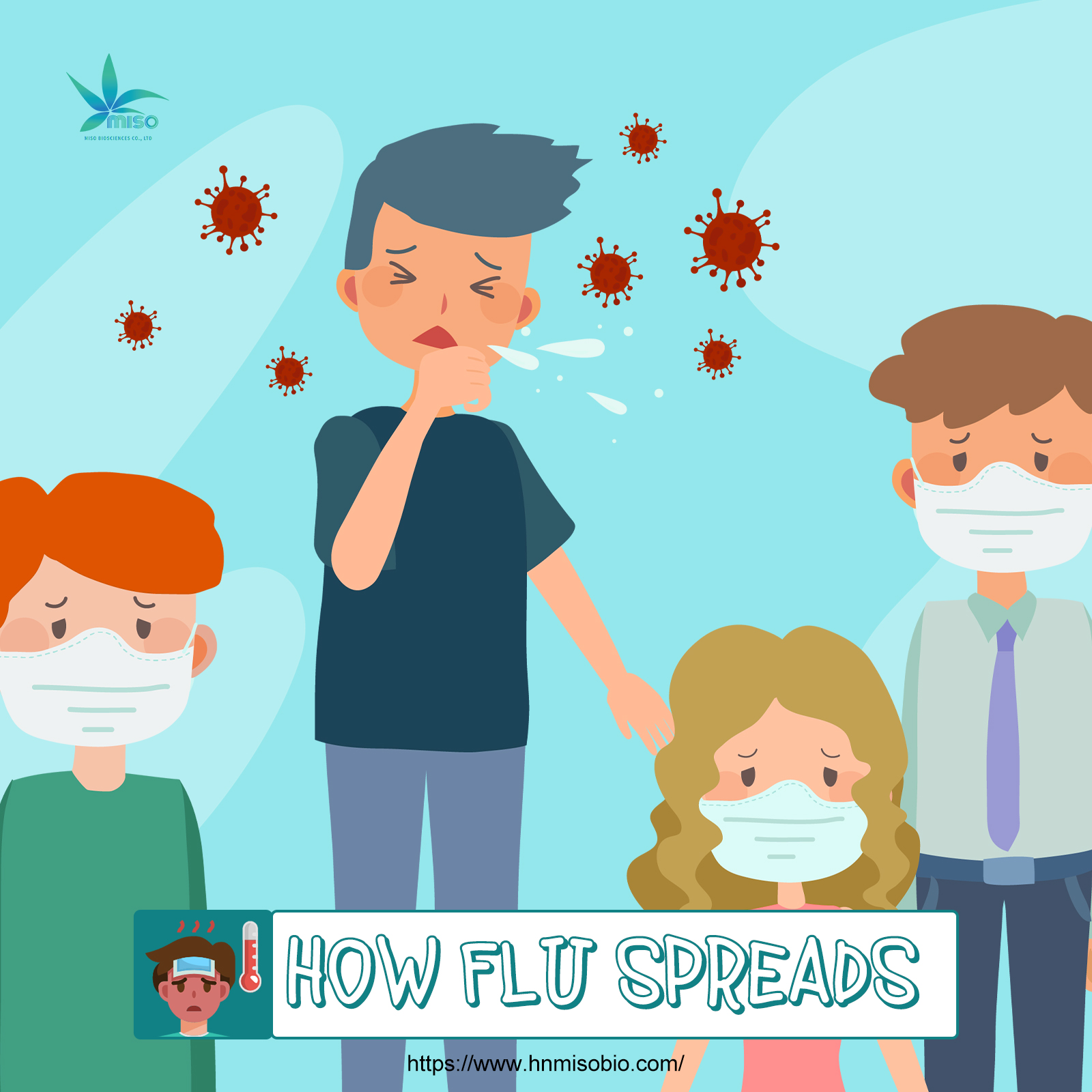
4. Transmission:
- The flu virus is primarily spread through airborne droplets, such as those released when someone coughs, sneezes, or talks.
- It can also spread by direct contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, followed by touching the eyes, nose, or mouth.

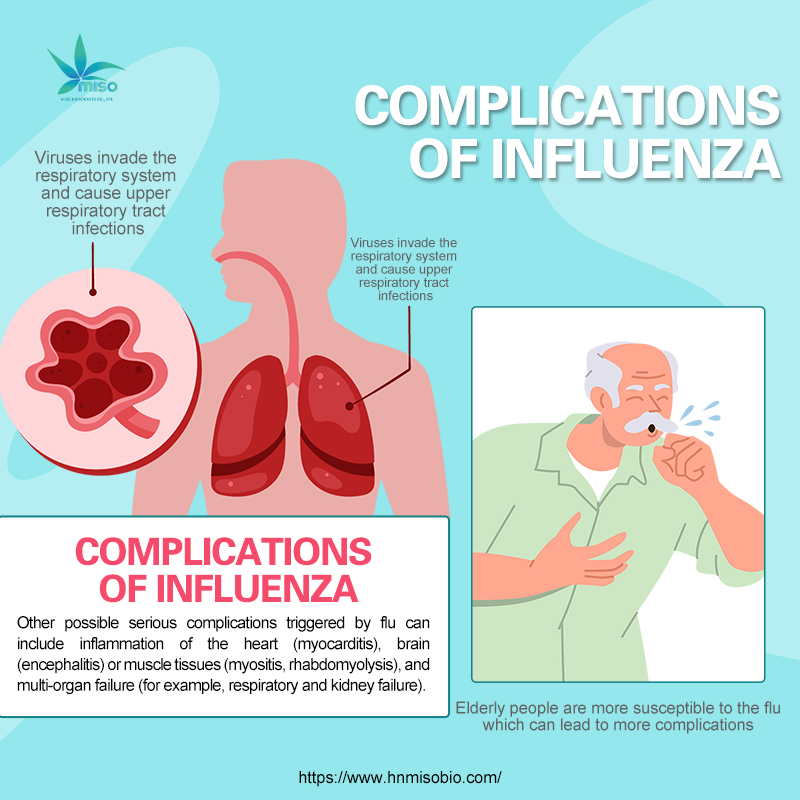
Risks and Complications of Influenza:
- Severe complications: Influenza can lead to serious complications, particularly in older adults, children, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Common complications include pneumonia, myocarditis, and otitis media.
- Risk of death: While most healthy adults can recover within a few days, certain high-risk groups (e.g., the elderly, those with chronic conditions) may face a higher risk of death due to complications.
Prevention and Treatment:
Understanding the symptoms, transmission methods, and prevention strategies for influenza can help better manage and prevent the spread of the flu.
Here are some common and effective ways to prevent influenza:
1. Get the Flu Vaccine:
- Getting the flu vaccine every year is the most effective way to prevent the flu. The vaccine helps boost your immunity and reduces the risk of infection, especially for high-risk groups such as the elderly, children, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems.
2. Wash Your Hands Frequently:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after touching public items, coughing, sneezing, or before eating. The proper way to wash your hands is to scrub for at least 20 seconds and dry them thoroughly.
3. Avoid Close Contact with Infected Individuals:
- Try to avoid close contact with people who are sick, especially during flu season. If you experience cold or flu symptoms, it's best to stay at home and avoid spreading the virus to others.
4. Maintain Good Personal Hygiene:
- When coughing or sneezing, cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow to prevent spreading the virus through airborne droplets or on your hands.
- Use disinfecting wipes to clean commonly touched surfaces, such as phones, doorknobs, and elevator buttons.

5. Boost Your Immune System:
- Maintain a healthy diet and get enough vitamins (like vitamin C and D) that support the immune system.
- Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management also help keep your immune system strong.
6. Practice Social Distancing:
- During flu season, try to avoid crowded places, especially when flu outbreaks are known to be occurring.
7. Avoid Touching Your Face:
- Hands can carry the virus from surfaces to your eyes, nose, or mouth, so avoid touching your face with unwashed hands to reduce the risk of infection.
By following these preventive measures, you can effectively reduce the risk of getting the flu, especially during peak flu season.